Zvec: The SQLite of Vector Databases
Abstract: Zvec is a lightweight, SQLite-like embedded vector database purpose-built for edge and on-device workloads. It delivers four core advantages: out-of-the-box usability, configurable resource budgets, extreme performance, and versatile vector capabilities. Open-sourced under the Apache 2.0 license, Zvec aims to provide developers with a one-stop path from prototyping to production deployment on the edge. Try Zvec—we’re excited to see your adoption, feedback, and contributions.
Background
Over the past few years, vector search has evolved from a backend component in search and recommendation systems into a foundational data infrastructure for intelligent applications. With the rise of RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), developers are no longer building vector systems solely for traditional search, recommendation, and advertising scenarios; instead, they are embedding "semantic memory" into a wide range of applications, including knowledge Q&A, semantic understanding, and AI assistants. Simultaneously, vector search technology is migrating from the cloud to terminal devices such as PCs and smartphones, driven by several key factors:
- Lower developer barrier: Frameworks like LangChain have made vector retrieval much easier to use, turning vector capability into a standard tool for developers.
- More compute at the edge: With the edge-AI trend, on-device compute keeps improving, enabling local vector computation and storage.
- Strict requirements for privacy and low latency: Healthcare/finance require on-device data processing; AR/autonomous driving requires ultra-low-latency responses.
Consider a typical edge scenario—a local RAG assistant on PC/mobile: users, even without a network connection, query local codebases, technical documents, or meeting notes via natural language. The system must store both vectors and scalar fields (e.g. time, file type, tags), support vector search and hybrid filtering by scalar attributes, and provide full CRUD because the knowledge base changes dynamically with local files. As an end-device application, memory and background resource usage must be tightly bounded, and data must be reliably recovered after crashes or forced exits. In addition, startup time and query latency must be low enough to fit seamlessly into a developer’s daily workflow.
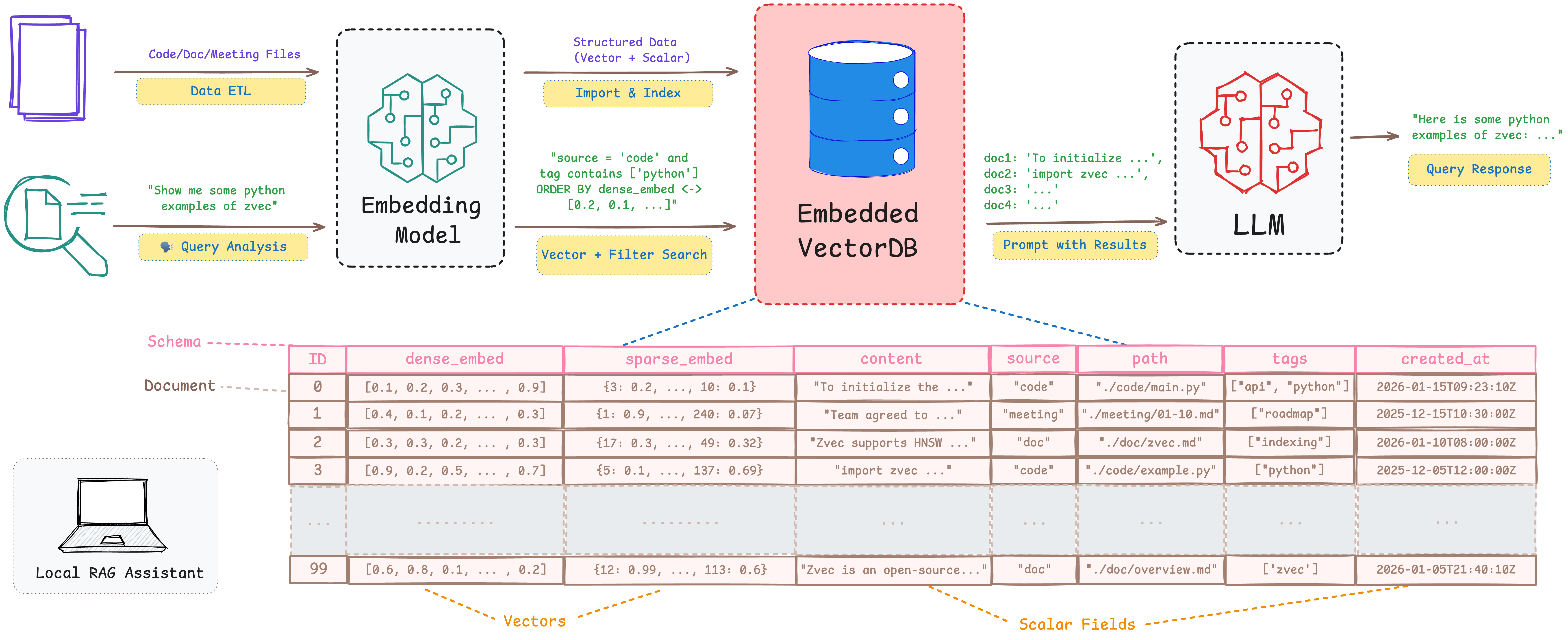
Today’s mainstream options leave real gaps in this setting:
- Index-only libraries (e.g. Faiss): Lack database fundamentals such as scalar storage, hybrid queries, full CRUD, and crash recovery—requiring substantial surrounding engineering to reach production readiness.
- Embedded solutions (e.g. DuckDB-VSS): Vector functionality is constrained (limited index choices, no quantization compression, and limited runtime resource control). On PCs, excessive memory/CPU usage can degrade overall system performance.
- Service-based (e.g. Milvus): Depend on separate processes and network communication, which introduces complexity and overhead. These systems don’t embed cleanly into CLI tools, desktop apps, or mobile clients—and operational burden is heavy, making them a poor fit for end-device environments.
What is Zvec?
To meet these requirements, we open-sourced Zvec—an embedded, ultra-high-performance, zero-dependency, production-ready vector engine that makes vector retrieval as simple, reliable, and ubiquitous as SQLite.
Zvec’s core goal is to make high-quality vector capabilities readily accessible, guided by the following principles:
- Embedded: Runs purely locally—no network, no standalone service, zero-config startup. Runtime resources (e.g. memory) are controllable; the API is minimal and easy to integrate and extend, enabling seamless embedding into edge apps, CLI tools, AI frameworks, or database systems.
- Vector-native: Designed end-to-end for vector workloads, offering rich, high-quality indexing and quantization options to meet different resource constraints, with deep adaptation across hardware platforms. Supports diverse retrieval modes for RAG, multimodal search, and more.
- Production-ready: Stability-first, with persistent storage, thread-safe access, and automatic crash recovery—ensuring long-term reliable operation in zero-ops environments such as phones, CLIs, and in-vehicle systems, avoiding data loss or inconsistent state after abnormal exits.
Why Zvec?
While staying easy to use, Zvec provides more complete retrieval capabilities, stronger resource governance, and better search performance than other edge vector database options. Key comparisons:
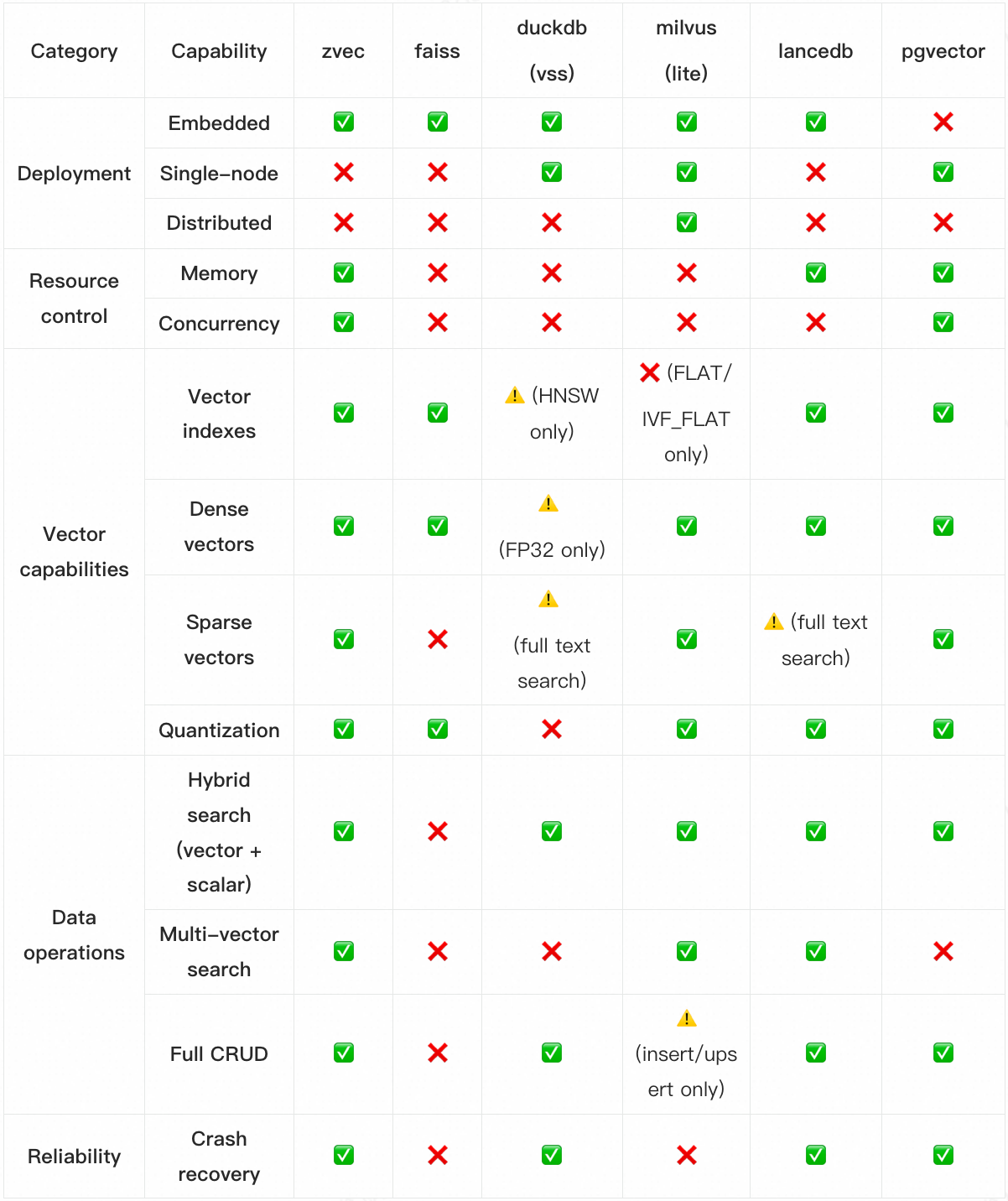
Out of the box: build a vector search app in one minute
With one-command installation (no service deployment, minimal dependencies) and a minimal API, Zvec delivers a truly out-of-the-box experience. Python users can embed vector capabilities directly via pip install zvec, and build a local semantic search prototype with just three API steps (create_and_open → insert → query)—from install to run in under a minute.
Zvec Python SDK (v0.1.0) is now available:
Install
pip install zvecOne-Minute Example
import zvec
# Define collection schema
schema = zvec.CollectionSchema(
name="example",
vectors=zvec.VectorSchema("embedding", zvec.DataType.VECTOR_FP32, 4),
)
# Create collection
collection = zvec.create_and_open(path="./zvec_example", schema=schema,)
# Insert documents
collection.insert([
zvec.Doc(id="doc_1", vectors={"embedding": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]}),
zvec.Doc(id="doc_2", vectors={"embedding": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.1]}),
])
# Search by vector similarity
results = collection.query(
zvec.VectorQuery("embedding", vector=[0.4, 0.3, 0.3, 0.1]),
topk=10
)
# Results: list of {'id': str, 'score': float, ...}, sorted by relevance
print(results)💡 For a more detailed quick-start, see Zvec QuickStart.
Extreme performance: built for real-time interaction on the edge
Powered by Proxima, a high-performance vector engine developed by Alibaba Tongyi Lab, Zvec significantly improves compute efficiency across indexing and querying through deep optimizations—including multi-threaded concurrency, memory layout optimization, SIMD acceleration, CPU prefetching, and more. It delivers low-latency, high-throughput vector retrieval, enabling real-time interactions even in resource-constrained edge environments.
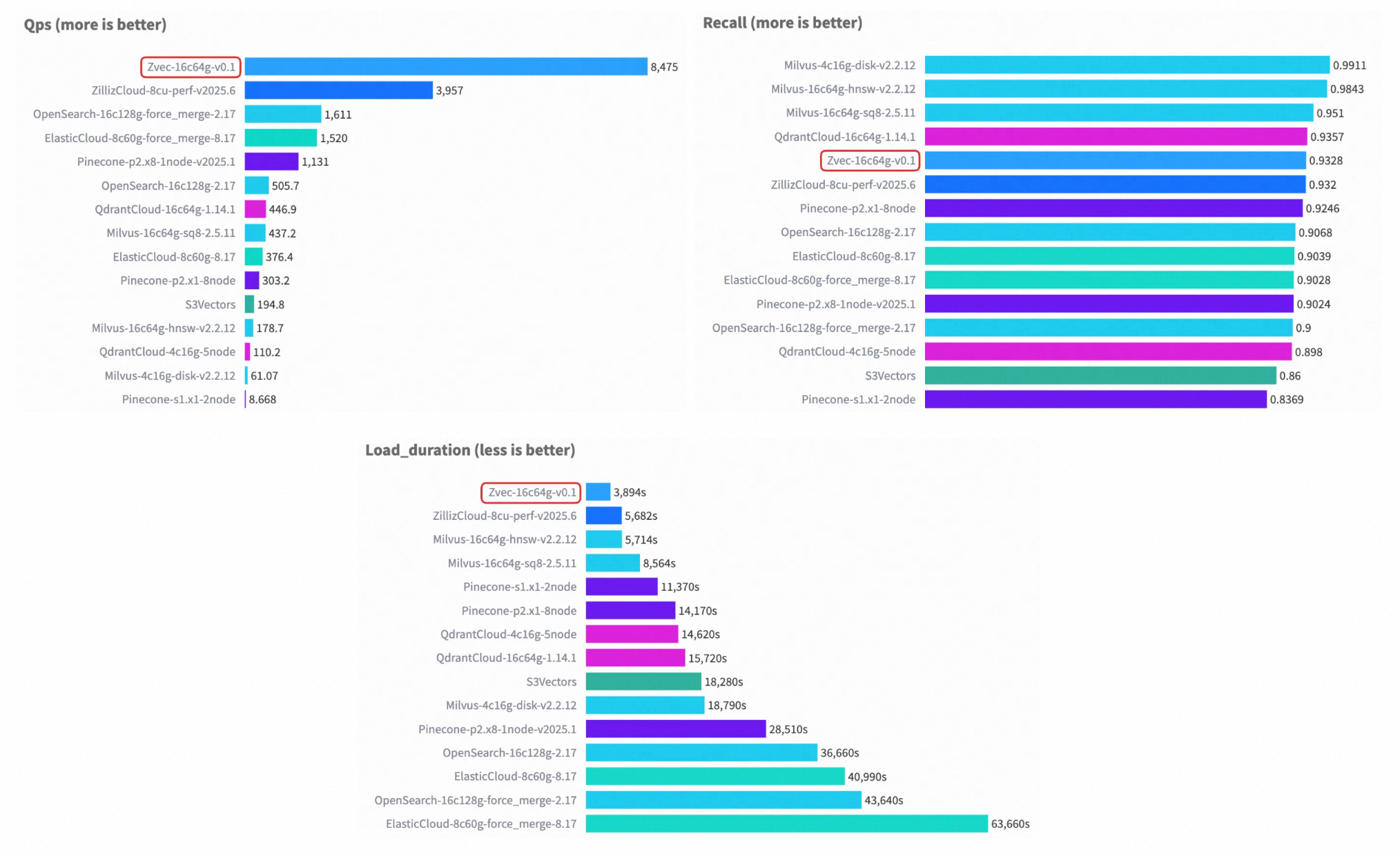
In a representative VectorDBBench setup (Cohere 10M dataset), under comparable hardware and matched recall levels, Zvec achieves over 8,000 QPS—more than 2× the previous leaderboard #1 (ZillizCloud)—while also substantially reducing index build time, demonstrating a comprehensive performance lead.
Cohere 10M Performance Case
Cohere 1M Performance Case
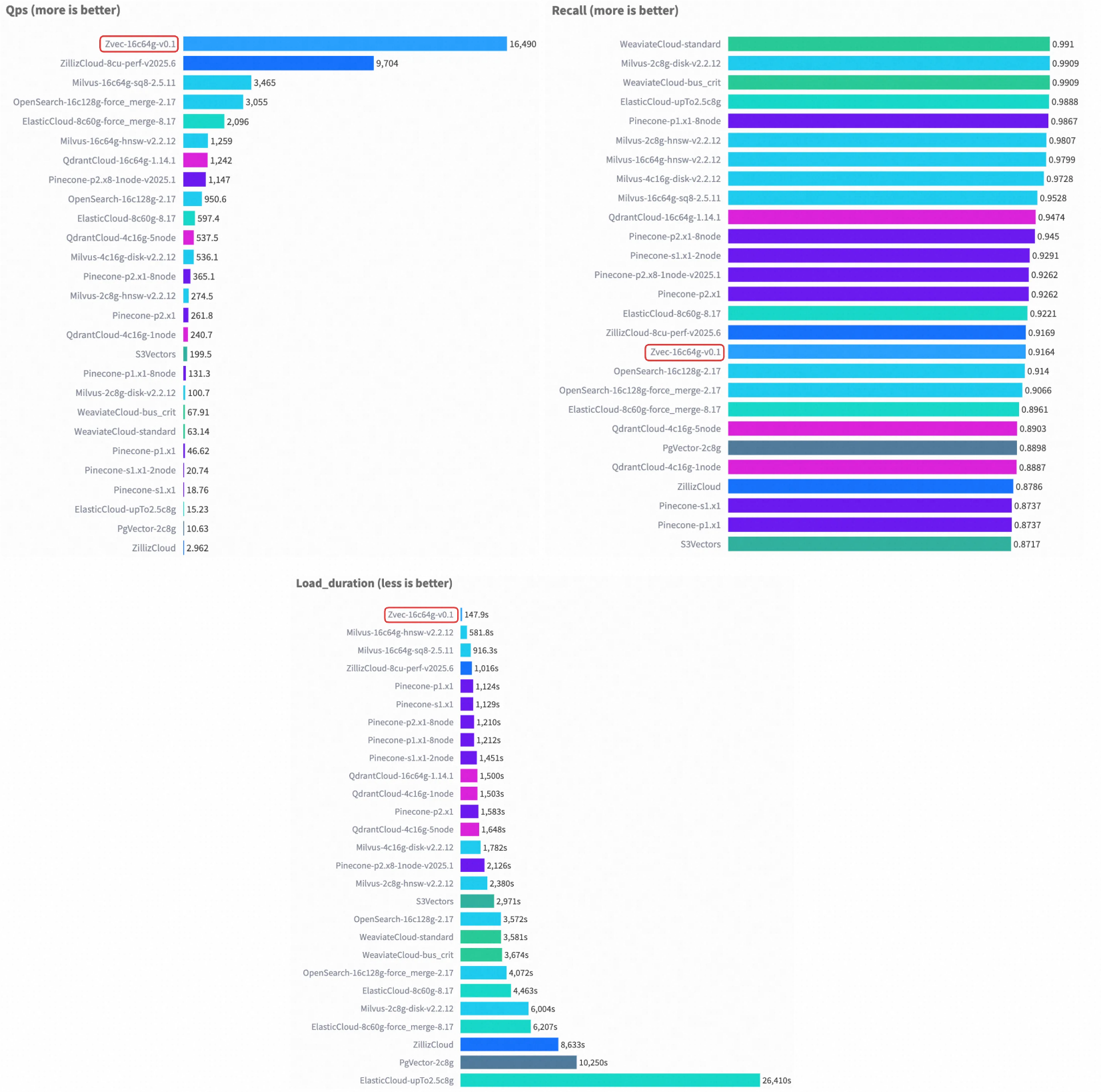
💡 For more benchmark details, see Zvec Benchmark.
Controllable resources: fit for CLI, mobile, and other constrained environments
In constrained environments such as mobile devices, serverless functions, or CLI tools, vector systems must have clear boundaries on memory and CPU usage; otherwise, applications can crash or be terminated by the system (e.g. Linux OOM Killer or Android ANR). Zvec includes resource constraints at the architectural level to ensure stable operation under tight budgets.
Memory control: adapt indexes to limited memory and avoid OOM
Graph indexes such as HNSW can temporarily consume several times the raw data size in memory during build or query. To prevent such unpredictable behavior, Zvec provides three layers of memory management:
- Streaming, chunked writes: By default, writes are processed in 64MB chunks to avoid holding all data in memory, balancing throughput and memory usage.
- On-demand loading via mmap: Enable memory-mapped mode with
enable_mmap=true. In this mode, vector and index data are paged into physical memory on demand by the OS, avoiding OOM even when total data exceeds available RAM. - Hard memory limiting [Experimental]: When
mmapis not enabled, Zvec enters a hard memory control mode. It maintains an isolated, process-level memory pool, and users can explicitly cap its budget viamemory_limit_mb.
Concurrency control: prevent thread overuse and keep the main thread responsive
In GUI applications (desktop tools, mobile apps), unconstrained vector computation may spawn many threads and saturate CPU, causing UI stutter or scheduler penalties. Zvec provides fine-grained concurrency tuning:
- Index build concurrency: All index creation APIs support a
concurrencyparameter to specify the number of build threads. A globaloptimize_threadssetting can cap maximum build concurrency within the process to prevent background tasks from starving foreground responsiveness. - Query concurrency: A global
query_threadssetting lets users cap the maximum number of query threads.
Application-ready: full vector capabilities for RAG
Zvec is designed with RAG as a primary target and covers the full RAG pipeline through the following capabilities:
Dynamic knowledge management
- Full CRUD enables real-time updates to private knowledge bases.
- Schema evolution is supported, allowing index strategies to adapt as metadata and query patterns evolve.
Multi-vector retrieval and fusion
- Native support for multi-vector joint queries enables multi-channel semantic retrieval and semantic+keyword retrieval in RAG.
- Built-in default reranker (supports weighted fusion and RRF) automatically fuses and ranks results, eliminating manual merging at the application layer.
Scalar-vector hybrid search
- Scalar filters can be pushed down into the vector index execution layer, avoiding full scans in high-dimensional space and significantly improving hybrid search efficiency.
- Scalar fields can optionally build inverted indexes to accelerate equality/range filtering and further optimize hybrid retrieval.
Feature overview
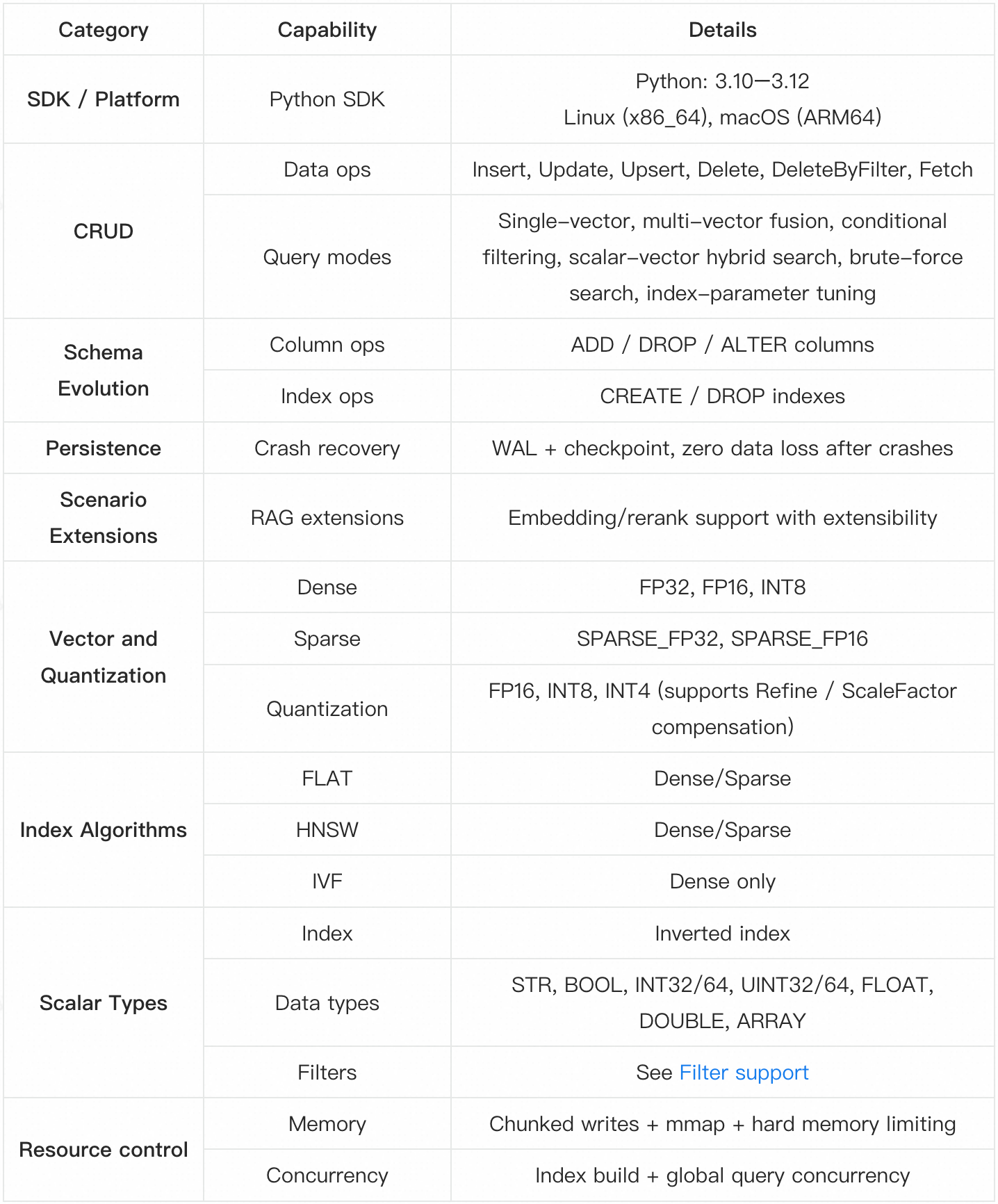
💡 More details are available in the Zvec Docs.
Roadmap
A truly “ready-to-use” vector database demands continuous refinement. Moving forward, we’ll focus on four key pillars for iterative development:
- Developer experience: Enhance CLI tooling and multi-language SDKs, deepen integrations with LangChain and LlamaIndex, and deliver polished extensions for common RAG and edge-AI scenarios.
- Deeper capability expansion: Strengthen indexing continuously, introduce vector-native features like grouped queries, and keep tracking major performance leaderboards.
- Ecosystem collaboration: Advance integrations with DuckDB and PostgreSQL via vector extensions, support external tables (e.g. Parquet, CSV), and contribute to a thriving open ecosystem.
- End-to-end validation in real deployments: Partner with ISVs and hardware vendors to deliver real edge cases (iOS/Android/Nvidia Jetson).
Join us
Zvec is open-sourced under Apache 2.0, with the goal of making vector capabilities universally accessible—lightweight, reliable, and free of licensing barriers.
Whether you’re a developer, user, or ecosystem partner, you’re welcome to participate:
- Code: C++/Python/Rust development, testing, performance optimization
- Docs: Tutorials, examples, API annotations
- Use cases: Share practices in RAG, recommendation, and on-device intelligence
- Ecosystem: Integrate with LangChain/LlamaIndex; collaborate with DuckDB/PostgreSQL, etc.
The project is just getting started—we look forward to building truly practical embedded vector infrastructure together.

